Full s.p. (from pursuing an activity)
The basis for calculating contributions for sole proprietors for the first calendar year is equal to the minimum wage. In the coming years, the basis is determined based on the performance of the business in the previous financial year, which is what basis of insurance you use to find out that the amount from the item 9 tax bills are added to the calculated social security contributions (in simplified speaking, all the contributions made for compulsory social insurance are added to the achieved profit from the previous year), and the resulting amount is reduced by 28% (valid for 2015). Written means that each individual has an individually determined amount of contributions. For sole proprietors who determine profits on the basis of standardized expenses, the same method is used to determine the class for the payment of contributions.
The minimum basis for contributions for self-employed persons is:
- in 2015: the amount of 54% of the last known average annual salary of employees in the Republic of Slovenia, calculated per month,
- in 2016: 56% PP,
- in 2017: 58% PP,
- in 2018: 60% PP.
This means that monthly contributions, with the exception of the first class, where they are paid from the minimum wage, change monthly and the entrepreneur must carefully monitor it. In the event that the profit achieved is zero or negative (loss), it means that the basis for determining the appropriate class is equal to the amount of social security contributions charged. For January 2015, the minimum insurance base is € 831.77 gross, which means that the minimum contributions for compulsory social insurance for self-employed are € 326.47 per month.
The highest insurance base for insured persons is 3.5 times the average annual salary of employees in the Republic of Slovenia calculated per month, which amounts to € 5,390.87 for 2015, contributions in the amount of 2.059,31 €.
A sole trader with a registered full s.p. can pay higher contributions for the first year as much as he wants.
If the entrepreneur has been in business for only a few months of a particular year, the contributions have to be converted to the number of months of business as shown in the example below. We take into account only the months and for at least 15 days of business is taken into account for the full month.
Example:
In 2014, the privately-owned company operated only three months, had a profit of 3,000 euros (amount entered in the 9th tax return) and had a total of € 950.58 in 2014.
3.000 € + 950,58 = 3.950,58 3.950,58*0,72/3= 948,14€ ,
This means that its basis for 2015 is € 948.14, while the amount of monthly social security contributions is 38.2% of this amount, 362,19 €.
For sole proprietors, who determine profits on the basis of standardized expenses, the latest decision on assessment of personal income tax is taken into account for the determination of the class for payment of contributions.
IMPORTANT!
The new classification in the insurance base is determined for the month following the month when the tax return was submitted to the FURS.
Types of contributions that a private person must pay:
|
The contributions payable by the enterprise are:
|
from BOD
|
on BOD
|
amount (min. base)
|
|
1. contribution of ZPIZ (from 54% PP)
|
15,50%
|
8,85%
|
202,53€
|
|
2. contribution of ZZ ( from 60% PP)
|
6,36%
|
6,56% + 0,53%
|
124,30€
|
|
3. contribution to employment (from 54% PP)
|
0,14%
|
0,06%
|
1,66€
|
|
4. contribution for parents protection
|
0,10%
|
0,10%
|
1,66€
|
|
Total
|
22,10%
|
16,10%
|
330,15€
|
Source: data.si
Afternoon s.p.
Afternoon s.p. is not a legal or legal term, so you can not find it in laws or legal acts. It is a talk term that identifies a sole proprietor who performs a complementary activity and does not pay contributions for social insurance alone, but is protected from another address.
This kind of activity is suitable for an individual who has paid social security contributions through employment in another company. Afternoon s.p. (supplementary activity or accessory profession) can only have a person who is in full-time employment (40 hours per week).
Afternoon s.p. usually open by those who do not work in the regular service, either because they do not have enough earnings or they have the desire to create on their own. Due to the relatively low costs of contributions (some 65 euro per month), this form of company is a kind of business-to-business polygon. In the event that the transaction succeeds, it can quickly expand its activity on a full-time basis or open up some other form of business.
The flat rate contribution for ZPIZ from 2015 is € 32.20. The flat-rate contribution for injuries at work and occupational illness from 2015 amounts to € 32.67, a total of € 64.87.
INCOME TAX
Exemption from payment of contributions when opening the company
From 1 July 2013 on the first entry into the business register, partial exemption from the payment of contributions for pension and disability insurance can be claimed.
The purpose of the partial exemption is to reduce the burden on self-employed persons when starting the business and encouraging entrepreneurship.
Persons who are compulsory pension and disability insurance as self-employed are:
- during the first 12 months of operation after the first entry in the business register or in another register or record, the payment of the contribution of the insured person for ZPIZ and the contribution of the employer in the amount of 50% of the amount of the contribution
- in the next 12 months, the contribution of the insured and the employer's contribution in the amount of 30 percent of the amount of the contribution
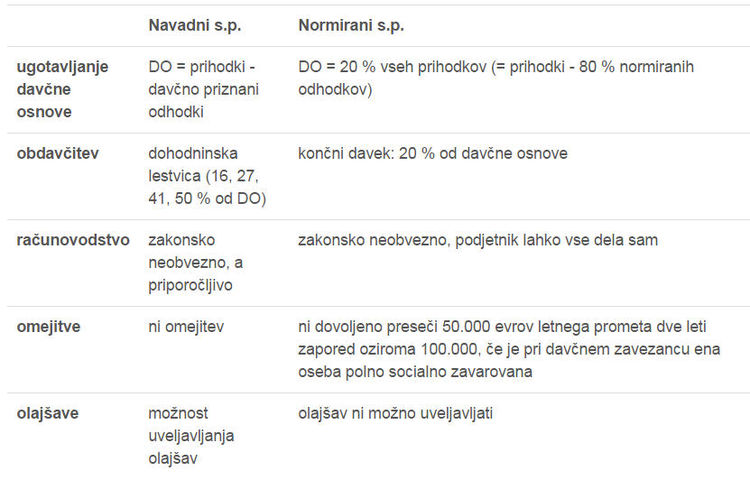
Differences between regular and standardized s.p.
(author: Maja Boršnik, Young Entrepreneur)
The main difference between standardized and ordinary s.p. are in determining the tax base and accounting. In the standardized tax base, the tax base (DO) is determined by deducting 80 percent of the standardized expenses from all tax-deductible revenues, and all tax-deductible expenses are deducted from all tax-deductible revenues. In ordinary s.p. the tax base can be reduced by applying the tax relief, but it is not possible for norms.
Normans, who are liable for VAT, must also keep records that are necessary for charging VAT, for example, a book of received and issued invoices. Some normants, for example, traders, caterers, etc., must also keep other records, in so far as they require special regulations in the field of their activities.
There is a limitation to determine the tax base on the basis of standardized expenses. Only a taxpayer who, in the fiscal year prior to this year, did not exceed the annual turnover threshold of EUR 50,000 can be decided for such a determination.
A further difference is in the taxation itself, whereby ordinary s.p. taxable on the income tax scale, and the normant is taxed with a final cedular tax of 20%.
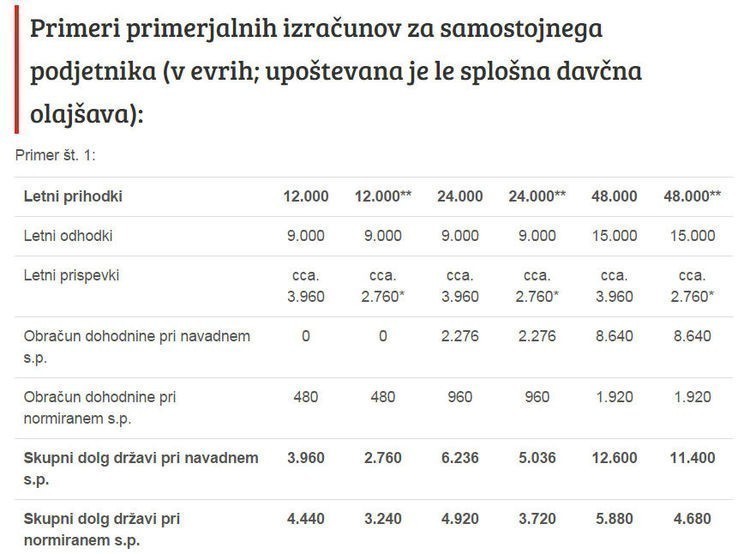
*newly created companies (in the first year of operations 50% exemption from payment of contributions for pension and disability insurance, and in the second year 30%; ** exempt PIZ contributions represent revenues, and therefore the real amount of annual revenues should be slightly lower
Summarized by: data.si and mladopodjetnik.si
 Make it easy for business beginners.At SRC Bistra Ptuj, promotion of entrepreneurship is one of the key activities. We help the future entrepreneurs to start a business or register as a sole proprietor / sole proprietors. We offer you advice on procedures when opening a company, register in the VAT system of taxpayers, the choice of registered activities, registration of employees. Within SPOT, we provide this service free of charge, because they are co-financed by SPIRIT Slovenia and MGRT.
Make it easy for business beginners.At SRC Bistra Ptuj, promotion of entrepreneurship is one of the key activities. We help the future entrepreneurs to start a business or register as a sole proprietor / sole proprietors. We offer you advice on procedures when opening a company, register in the VAT system of taxpayers, the choice of registered activities, registration of employees. Within SPOT, we provide this service free of charge, because they are co-financed by SPIRIT Slovenia and MGRT.